Before implementing this article, have a look at database, keys and sql command by going through the below article
Understanding database, SQL and its commands
This article is a continuation of the above article. So first go through the above article so that clear understanding of select and show commands can be achieved. For SQL filtering with queries, select command will be used very often. Filtering helps to provide only the desired results. In this article we will implement where clause, between, in, and, or operator to apply filters to the results.
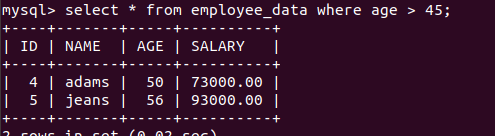
WHERE CLAUSE
It will retrieve those results which are based on condition applied using where clause.
Let us see the syntax
select * from table where condition
This statement selects all records which fulfils the particular condition which one can mention in the where clause. Have a look at the below screenshot
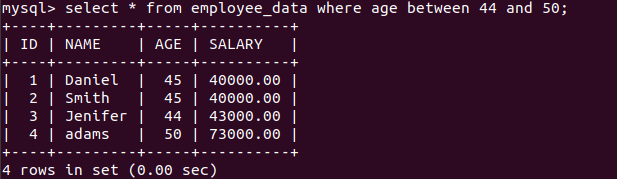
BETWEEN OPERATOR
It will retrieve those results which are based on lower and upper bounds set by the between operator. One can choose the bound accordingly. Remember that both the upper and lower bound is included during retrieval. It is used with the where clause.
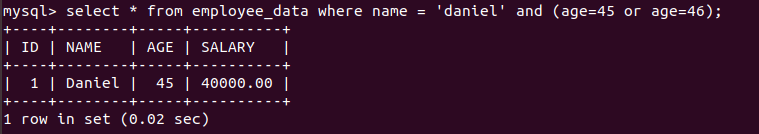
CONJUNCTIVE OPERATORS
Operators (or and) are called conjunctive operators. They can be used together in the query to filter the results based on the condition applied.
IN OPERATOR
It is used when you want to compare a column field for more than one value. You can achieve the same result using OR operator but the length of query will increase.
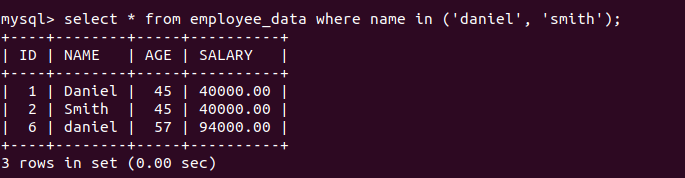
NOT IN OPERATOR
It is used when one needs to exclude list of values from a column fields during data retrieval.
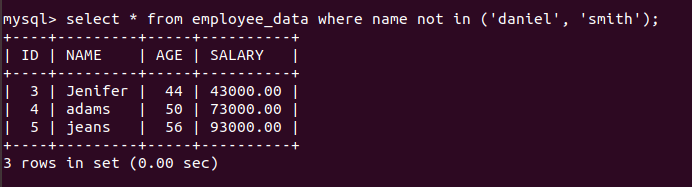
Point to note: When one is implementing sub query inside a query then enclose the subquery using parentheses.
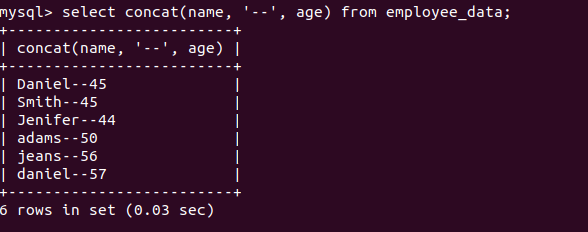
CONCAT FUNCTION
It is used to concat two or more text values and returns the concatenated string.
So, from this article one can learn how to filter data using SQL queries and how to apply subqueries in the query taking into consideration that parenthesis is to be applied for a sub query. In the next coming post joins will be discussed. Read the basics of SQL and its commands from below